If you’re a business owner, marketer, or salesperson, you know that understanding consumer behaviour is crucial to achieving success. Consumer behaviour theories provide valuable insights into why people behave the way they do when making purchasing decisions. By knowing and applying these theories, you can better understand your target audience, tailor your marketing messages, and ultimately drive more sales for your business. So let’s get started!
INTRODUCTION
Understanding consumer behaviour is essential for any business that wants to succeed. By understanding why people make the purchasing decisions they do, businesses can tailor their marketing strategies to better meet the needs and desires of their target audience. Consumer behaviour theories provide a framework for understanding why consumers behave the way they do.
Have you ever wondered why you tend to choose one brand over another when buying a product? That’s where consumer behaviour theories come in. In this article, we’ll cover 7 consumer behaviour theories you need to know.
WHAT IS CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR?
Consumer behaviour refers to the actions and decisions that consumers make when purchasing goods or services. It is influenced by a variety of factors, including personal factors such as age, gender, and income, as well as social factors such as culture and social class. Consumer behaviour theories help us understand why consumers make the decisions they do, and how we can influence those decisions through marketing and sales strategies.
Ready to take your marketing to the next level? Book a free 30-minute strategy session with our team today! During the session, we’ll discuss your business goals and needs and we will develop a custom digital marketing plan specifically for you. for an effective marketing strategy. There’s no obligation and it’s completely free, so why wait? Claim it now!
1. MASLOW’S HIERARCHY OF NEEDS THEORY
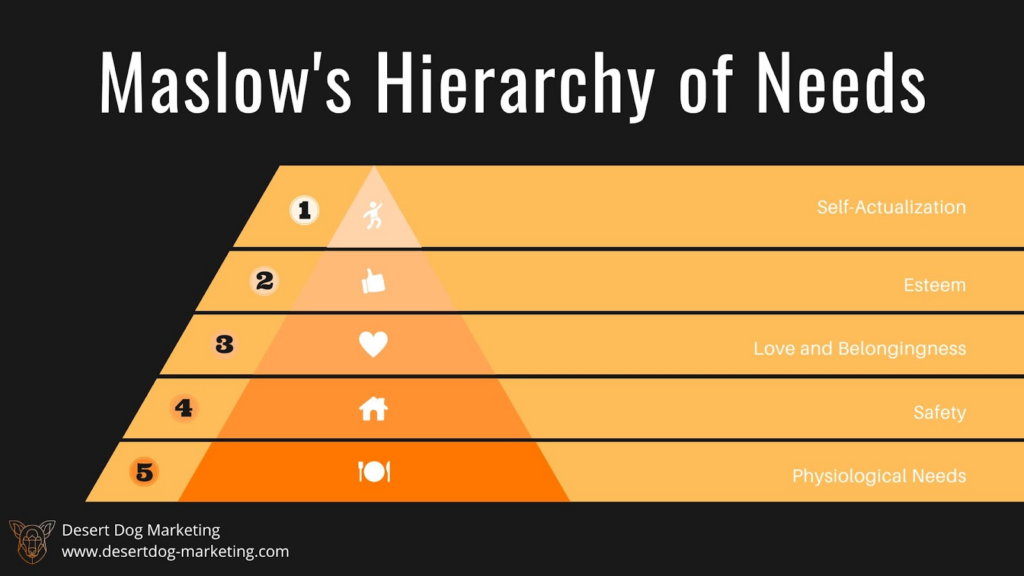
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory is one of the most well-known consumer behaviour theories. According to Maslow, human needs can be organized into a hierarchy, with basic physiological needs such as food, water, and shelter at the bottom, and the goal at the top: self-actualization. Maslow believed that people are motivated to satisfy their needs in order of priority, and that they will only move on to higher-level needs once their basic needs are met. Once all other needs are met then one can achieve self-actualization.
This could be seen when people prioritize their spending based on their needs. For example, someone who is struggling to pay for food and rent will likely not be interested in buying luxury items like expensive jewelry or designer clothes. Instead, their focus will be on meeting their physiological needs such as food, water, and shelter.
On the other hand, someone who has their basic needs met may be more interested in fulfilling their higher-level needs such as personal growth. They may invest in experiences like travel, education, or personal development programs.
2. THE SELF-DETERMINATION THEORY
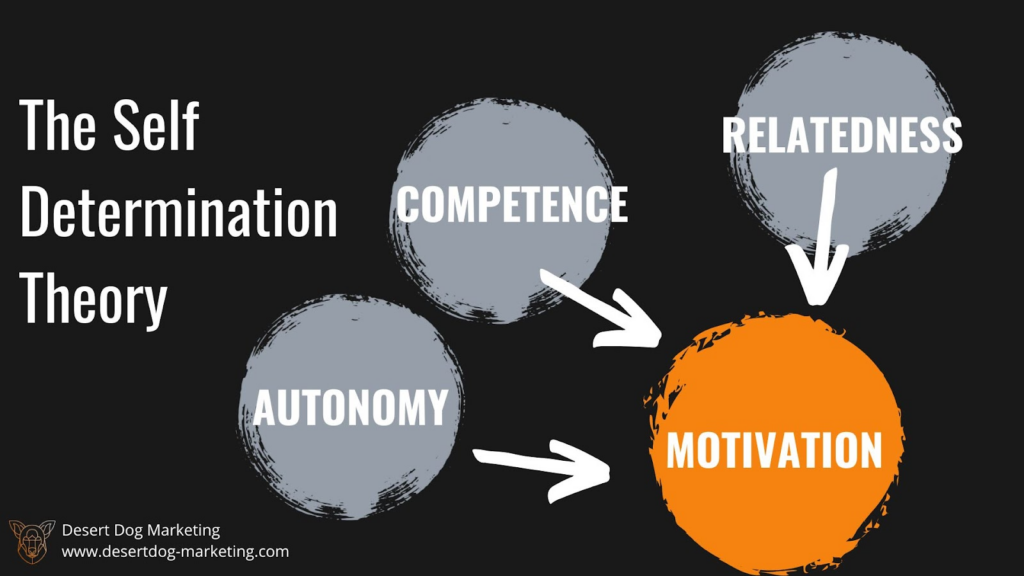
The Self-Determination Theory is based on the idea that people have three basic psychological needs: autonomy, competence, and relatedness. Autonomy refers to the need to have control over one’s own life, while competence refers to the need to feel competent and effective in one’s actions. Relatedness refers to the need for positive social interactions and relationships. According to the Self-Determination Theory, people are most motivated when their basic psychological needs are met.
For example, a brand that promotes a sense of autonomy, competence, and relatedness can be more appealing to consumers.
AUTONOMY
A company that offers a wide range of product options and allows customers to make their own choices can foster a sense of autonomy. This can make customers feel empowered and more satisfied with their purchasing decisions.
COMPETENCE
Similarly, a brand that focuses on product quality and provides customers with the resources and support they need to use the product effectively can help fulfill their need for competence. This can lead to greater customer satisfaction and loyalty, as customers feel confident in their decision to choose that brand.
RELATEDNESS
Lastly, a company that promotes a sense of relatedness by emphasizing its values and connecting with customers on a personal level can help foster a sense of belonging and community. This can lead to increased brand loyalty and positive word-of-mouth marketing.
By understanding the basic psychological needs of consumers and incorporating the principles of the Self-Determination Theory into their marketing strategies, businesses can create a more engaging and satisfying customer experience, which can ultimately lead to increased sales and long-term success.
3. THE THEORY OF PLANNED BEHAVIOUR
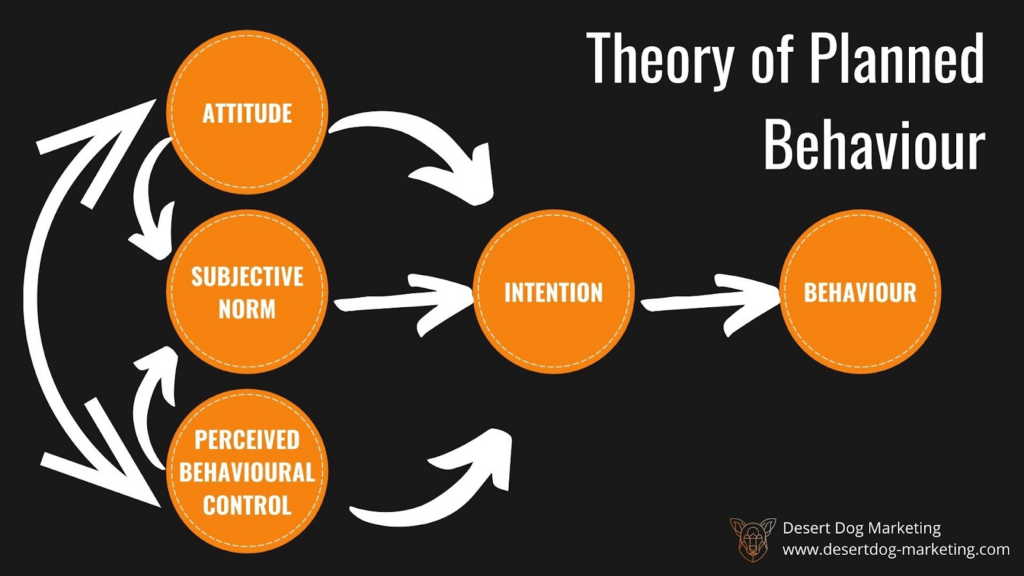
The Theory of Planned Behaviour is based on the idea that people’s intentions are influenced by their attitudes towards the behaviour, their subjective norms (i.e. what they perceive others think about the behaviour), and their perceived behavioural control (i.e. how easy or difficult it is to perform the behaviour).
As an example, let’s look into the decision-making process of purchasing a new car. Suppose a person is considering buying an electric car for the first time. According to the theory, their intention to buy an electric car will be influenced by their attitude towards the following:
Attitude: The person’s attitude towards electric cars will be an important factor in their intention to buy one. If they have a positive attitude towards electric cars and believe that they are environmentally friendly and cost-effective in the long run, they are more likely to intend to buy one.
Subjective norms: The person’s perception of what others think about electric cars will also influence their intention to buy one. If their family and friends have positive opinions about electric cars, they may feel more comfortable and confident in their decision to buy one.
Perceived behavioural control: Finally, the person’s perceived behavioural control will also play a role in their intention to buy an electric car. If they feel that they have the necessary resources and knowledge to own and operate an electric car, they are more likely to intend to buy one.
A car dealership could emphasize the environmental benefits and long-term cost savings of electric cars to appeal to consumers’ positive attitudes towards the behaviour. Additionally, they could leverage social proof and testimonials from satisfied customers to influence consumers’ subjective norms. Finally, they could provide educational resources and support to help consumers feel more confident in their ability to own and operate an electric car, thereby increasing their perceived behavioural control.
4. THE ELABORATION LIKELIHOOD MODEL
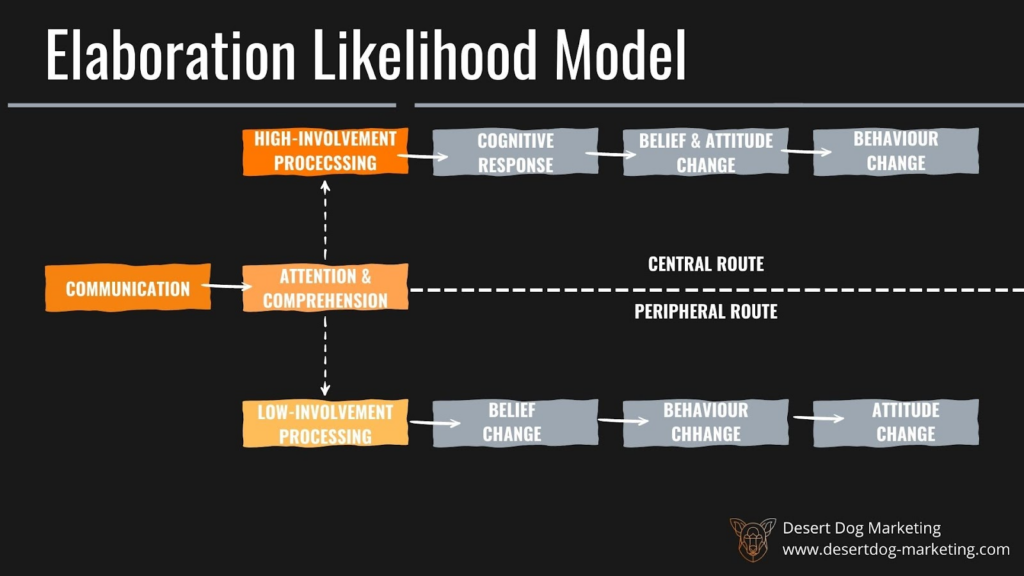
The Elaboration Likelihood Model is based on the idea that people process information differently depending on their level of involvement in the decision-making process. According to the model, people process information either centrally (i.e. focusing on the content of the message) or peripherally (i.e. focusing on peripheral cues such as the source of the message). The model suggests that marketers can use different strategies to appeal to consumers depending on their level of involvement in the decision-making process.
This is typically visible when a person is considering purchasing a high-involvement product, such as a car or a house. In this case, the person is more likely to process information centrally and focus on the content of the message. Marketers can use detailed and informative advertisements to appeal to this type of consumer. However, for low-involvement products, such as a pack of gum, the person is more likely to process information peripherally and focus on cues such as the color and packaging of the gum. Marketers can use eye-catching packaging and branding to appeal to this type of consumer.
5. THE SOCIAL IDENTITY THEORY

The Social Identity Theory is based on the idea that people’s self-concept is partially derived from their membership in social groups. According to the theory, people tend to view members of their social group in a positive light, and may even adopt the values and attitudes of that group as their own. This is referred to as their ‘in group’.
Marketers can use this theory to appeal to consumers’ social identities by creating advertisements that feature members of the group, or by using language and imagery that is specific to the group.
For example, a sports brand may create an advertisement featuring a famous athlete who is part of the consumer’s favorite team, or a clothing brand may use the colors and logos associated with a popular fandom to create merchandise that appeals to fans of that group. By targeting specific social groups, marketers can create a sense of belonging and community among consumers, which can increase brand loyalty and sales.
6. THE PROSPECT THEORY

The Prospect Theory is based on the idea that people’s decisions are influenced by how they perceive the potential gains or losses of a given situation. According to the theory, people are more likely to take risks when faced with potential losses, and are more risk-averse when faced with potential gains. This theory has important implications for marketers, as it suggests that the way information is presented can have a significant impact on consumer behaviour.
If a company wants to encourage consumers to purchase a new product, they may offer a limited-time discount or a “buy one, get one free” promotion. By presenting these promotions as potential gains, consumers may be more likely to make a purchase.
On the other hand, if a company wants to encourage consumers to upgrade to a newer version of a product, they may highlight the potential losses of not upgrading, such as missing out on new features or falling behind competitors. By presenting the situation in terms of potential losses, consumers may be more likely to take the risk and make the upgrade.
7. THE STIMULUS-ORGANISM-RESPONSE MODEL
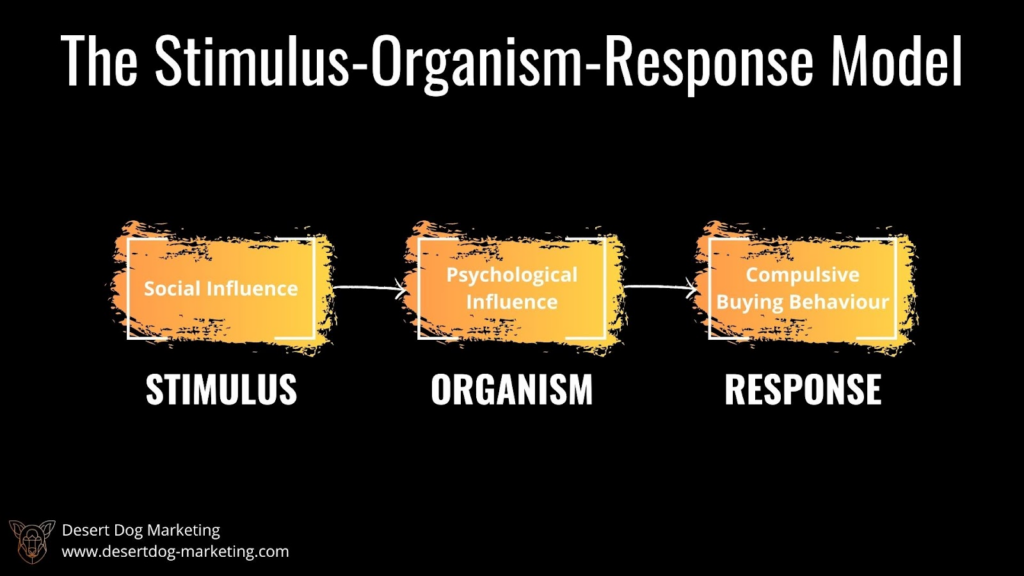
The Stimulus-Organism-Response Model is based on the idea that consumer behaviour is influenced by three factors: stimuli (i.e. marketing messages and other external factors), the consumer’s internal psychological state (i.e. their beliefs, attitudes, and emotions), and the consumer’s response (i.e. their behaviour). This model suggests that marketers can influence consumer behaviour by carefully designing marketing messages that appeal to consumers’ beliefs, attitudes, and emotions.
By understanding how these three factors interact, marketers can create more effective campaigns that appeal to consumers on a deeper level. For example, a company that sells environmentally-friendly products could create marketing messages that appeal to consumers’ beliefs and attitudes about sustainability. They could use images and language that evoke positive emotions, like happiness and satisfaction, to encourage consumers to make a purchase.
CONCLUSION
Understanding consumer behaviour is essential for anyone involved in marketing or sales. By understanding the theories that underlie consumer behaviour, marketers can create more effective marketing campaigns, increase sales, and build better relationships with their customers. In this article, we’ve covered 7 important consumer behaviour theories that you need to know. By applying these theories to your marketing strategies, you can better understand and influence the behaviour of your target audience.
FAQS

1. WHAT ARE THE KEY FACTORS THAT INFLUENCE CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR?
Consumer behaviour can be influenced by a wide range of factors, including cultural, social, personal, and psychological factors. These factors can include things like social norms, personal values, individual beliefs, and attitudes towards a product or service.
2. HOW CAN BUSINESSES CONDUCT MARKET RESEARCH TO BETTER UNDERSTAND CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR?
Businesses can conduct market research through a variety of methods, including surveys, focus groups, and online analytics. By gathering data on consumer behaviour and preferences, businesses can make more informed decisions about their marketing strategies.
3. HOW DO EMOTIONS INFLUENCE CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR?
Emotions can play a significant role in consumer behaviour. For example, positive emotions such as happiness or excitement can make consumers more likely to make a purchase, while negative emotions such as fear or anxiety can make consumers more risk-averse.
4. WHAT IS THE ROLE OF SOCIAL MEDIA IN INFLUENCING CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR?
Social media has become an increasingly important factor in consumer behaviour. By providing consumers with easy access to information about products and services, social media can influence consumer decision-making and purchasing behaviour.
5. HOW CAN BUSINESSES USE CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR THEORIES TO IMPROVE THEIR MARKETING STRATEGIES?
Businesses can use consumer behaviour theories to develop more effective marketing strategies by tailoring their messages to appeal to specific consumer needs and desires. By understanding the factors that influence consumer behaviour, businesses can create more compelling marketing messages that resonate with their target audience.


